Catastrophe bonds were first issued in the mid 1990’s. We’ve been actively tracking the catastrophe bond market since 1996 and now have a comprehensive database containing the details of almost every deal, featuring now over 650 catastrophe bond transactions.
Major catastrophe events in the 1990’s that struck the U.S., such as the Northridge earthquake and Hurricane Andrew, were seen as industry loss events of such potential magnitude that the insurance and reinsurance industry began to look for alternative methods to hedge their risks.
There was also a realisation that even larger catastrophe events were possible, which could severely drain the insurance and reinsurance market’s capital base, making access to the deepest and most liquid pool of capital available an attractive proposition.
Through collaboration between the reinsurance industry, capital markets structuring firms and investment banks, catastrophe bonds were born, with the first full 144a cat bond being issued in late 1996.
Catastrophe bond triggers
One of the key elements of any catastrophe bond is the terms under which the securities begin to experience a loss.
Catastrophe bonds utilise triggers with defined parameters which have to be met to start accumulating losses. Only when these specific conditions are met do investors begin to lose their investment.
Triggers can be structured in many ways from a sliding scale of actual losses experienced by the issuer (indemnity) to a trigger which is activated when industry wide losses from an event hit a certain point (industry loss trigger) to an index of weather or disaster conditions which means actual catastrophe conditions above a certain severity trigger a loss (parametric index trigger).
Catastrophe bond coverage
A catastrophe bond can be structured to provide per-occurrence cover, so exposure to a single major loss event, or to provide aggregate cover, exposure to multiple events over the course of each annual risk-period.
Some catastrophe bond transactions work on a multiple loss approach and so are only triggered (or portions of the deals are) by second and subsequent events. This means that sponsors can issue a deal that will only be triggered by a second landfalling hurricane to hit a certain geographical location, for example.
Catastrophe bonds can be designed to provide insurance, reinsurance or retrocessional protection to the ultimate beneficiary of the coverage. In some cases additional parties are brought to a cat bond deal to enable coverage to cascade down to a corporate sponsor, for example.
Catastrophe bond structure
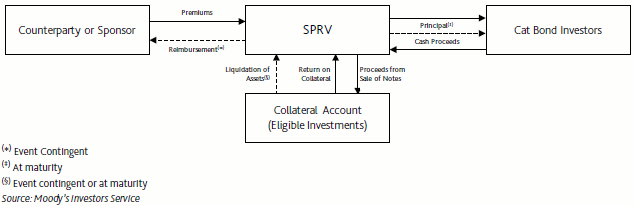
The typical catastrophe bond structure sees a special purpose vehicle or insurer (SPV or SPI) enter into a reinsurance agreement with a sponsor (or counterparty), receiving premiums from the sponsor in exchange for providing the coverage via the issued securities. The SPV issues the securities to investors and receives principal amounts in return. The principal is then deposited into a collateral account, where they are typically invested in highly rated money market funds.
The investors coupon, or interest payments, are made up of interest the SPV makes from the collateral and the premiums the sponsor pays.
If a qualifying event occurs which meets the trigger conditions to activate a payout, the SPV will liquidate collateral required to make the payment and reimburse the counterparty according to the terms of the catastrophe bond transaction.
If no trigger event occurs then the collateral is liquidated at the end of the cat bond term and investors are repaid.
The diagram below shows a typical catastrophe bond structure including where the capital flows from one party to another.
Catastrophe modelling is vital to catastrophe bond transactions to provide analysis and measurement of events which could cause a loss as well as to define the exposed geographical region.
Catastrophe bond structures have been used to hedge risks of natural catastrophe risks, such as hurricane, earthquake, typhoon, European windstorm, thunderstorm, hail, and also life insurance related risks, such as mortality, longevity and health insurance claims.
Increasingly the use of catastrophe bonds is broadening and the types of risks featured expanding, with recent arrangements having featured third-party liability risks, terrorism risks and financial guarantee exposures.
Read about recent and historic catastrophe bond transactions in our Deal Directory.
Keep up with all the latest catastrophe bond market news from Artemis.
 View all of our Artemis Live video interviews and subscribe to our podcast.
View all of our Artemis Live video interviews and subscribe to our podcast.
All of our Artemis Live insurance-linked securities (ILS), catastrophe bonds and reinsurance video content and video interviews can be accessed online.
Our Artemis Live podcast can be subscribed to using the typical podcast services providers, including Apple, Google, Spotify and more.