The retrocessional reinsurance market has become increasingly dependent on the capital markets and insurance-linked securities (ILS), with third-party capital providers beginning to dominate that sector and reinsurers increasingly utilising third-party capital backed retrocession.
Alternative capital in reinsurance played a significant role in reinsurance firms retro recoveries after the major hurricanes and catastrophes of 2017, cementing its role as a key provider of backstop coverage for the world’s largest reinsurers.
Following those major losses the amount of alternative capital in reinsurance and retrocession has continued to grow, as Standard & Poor’s highlighted in a recent report.
Data from S&P’s report shows the important and growing role that ILS and third-party capital has in reinsurance firms retrocessional arrangements, which the rating agency says shows “the retrocession market is increasingly dependent on third-party capital” and demonstrates the growth seen in the last two years in the chart below.
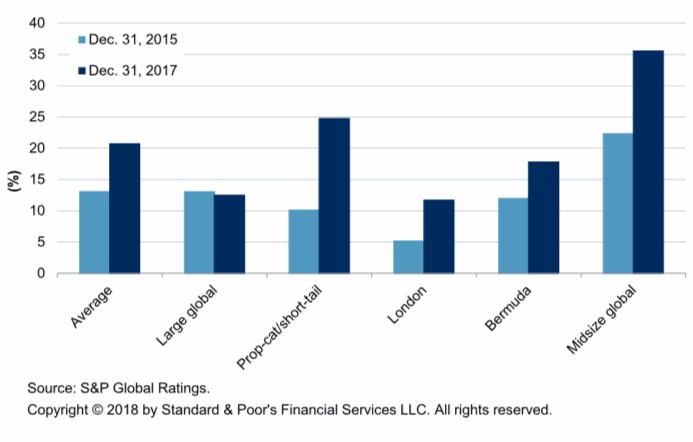
Average collateralized tail protection purchased by top-20 global reinsurers - % of collateralized recoveries at 1-in-250 year return period
As the chart above shows, global reinsurance firms have all increased their use of collateralized coverage at the 1-in-250 year return period, based on recoveries seen by S&P.
On average, the percentage of collateralized retrocession in reinsurers recoveries increased from 14% at the end of 2015 to 21% at the end of 2017, a 50% increase in the prevalence of fully collateralized retro at this level in their protection.
Breaking down the reinsurers you can see that the property catastrophe, short-tail line focused reinsurance firms have more than doubled their use of collateralized retrocession, from 10% of their recoveries at the end of 2015, to 25% at the end of 2017.
London-based reinsurers have also more than doubled their use of collateralized retro, according to these figures, while Bermudians have increased it in-line with the averages and the mid-sized global reinsurers continue to leverage more collateralized protection as well.
Interestingly though and perhaps contrary to other evidence, S&P has the large global reinsurers as utilising slightly less collateralized retro at this return period.
As we wrote the other day, Munich Re uses more sidecars and collateralized retro than before, as does Hannover Re, so this isn’t a clear picture of all of the major global reinsurers shrinking the prevalence of collateralized retrocession in their recoveries, it is perhaps just prevalent at this particular return period. Or the data isn’t adequately capturing these reinsurers private ILS arrangements and sidecars.
The top-20 reinsurers expanded their sidecar activities following the losses of 2017, as investors were keen to back the underwriting of the major players even following the hurricanes.
“Despite the 2017 losses, in aggregate, the top-20 reinsurers successfully expanded the use of sidecars or formed new vehicles, enabling them to expand their business while managing their net exposures,” S&P explained.
The rating agency also noted that, “Sidecars enable reinsurers that already have catastrophe exposure to take advantage of third-party capital to underwrite more risk at the front end. They can allocate capital according to the differing risk preferences while earning a fee income and receiving capital benefits for the retrocession purchased.”
The trifecta of motives for reinsurers establishing and growing sidecars and third-party capital vehicles are the ability to share in their performance with investors willing to put up full collateral, earn fee income while doing so, and source retrocession to help in their capital optimisation as well.
These motives aren’t going away and when returns on some peak catastrophe zone property catastrophe programs are not always returning enough to justify the cost of equity bearing them, a third-party capitalised balance-sheet vehicle (such as a sidecar, or collateralised retro product) is an attractive option that enables a reinsurer to maintain its market share, manage its PML exposure and still earn some income for its risk analysis, underwriting and origination expertise.
As a result the growth of collateralised retrocessional reinsurance is expected to continue and in time to come the capital markets will likely dominate this marketplace, at least in catastrophe risks and shorter-tailed specialty lines.
 View all of our Artemis Live video interviews and subscribe to our podcast.
View all of our Artemis Live video interviews and subscribe to our podcast.
All of our Artemis Live insurance-linked securities (ILS), catastrophe bonds and reinsurance video content and video interviews can be accessed online.
Our Artemis Live podcast can be subscribed to using the typical podcast services providers, including Apple, Google, Spotify and more.































