Since the January 1st 2015 reinsurance renewal global reinsurers have increased their use of retrocession for tail protection across all perils, as rates declined resulting in a buyers market and the use of alternative capital and ILS structures increased, according to S&P.
Financial services ratings agency Standard & Poor’s (S&P), in a recent report, notes the increased use of retrocessional reinsurance among many global companies during the January renewal period and beyond, driven in part by the persistent influx of alternative reinsurance capital and ILS backed capacity.
“As of Jan. 1, 2015, use of retrocession for tail protection (that is, to cover low-probability, high-severity exposures at a 1-in-250 year return period) across all perils had increased, reflecting the cheaper retrocession rates available globally and the increased use of third-party vehicles such as catastrophe bonds and side cars,” S&P explained, and highlighted in the chart below.

Average tail protection by peril (% recoveries at 1-in-250 yr return period)
This additional chart from a Standard & Poor’s infographic also graphically illustrates the increasing use of catastrophe retrocession, as the rate-on-line for catastrophe reinsurance underwritten declined.
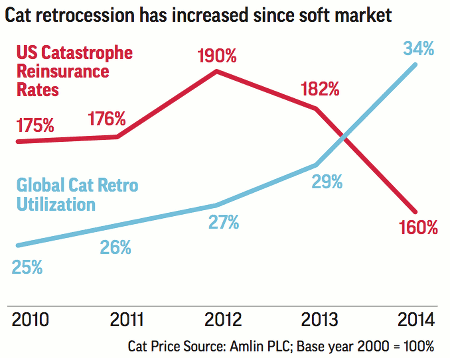
Increasing use of catastrophe retrocession reinsurance
The ample capacity currently sitting in the global reinsurance market, from a host of traditional and alternative capital providers, continues to pressure pricing across multiple business lines, retrocession included. And as the flow of capital into the sector is likely to persist, further weighing on retrocession pricing, S&P predicts reinsurers’ increased use of retrocession will continue.
In fact, with perhaps as much as half of global retrocessional reinsurance capacity provided by third-party capital investors, through insurance-linked asset managers and their funds, the availability of retro is likely to increase and the costs remain low.
Alongside a desire to more radically adjust reinsurance and retrocession buying, as part of the overall desire to ensure that as much premium is extracted from the risks underwritten and the right layers of peak risk laid off to others, retro is increasingly playing the role of capital management tool as well as risk transfer.
Underlining the amplified use of retrocession during 2015, notes S&P, is the “increased use of third-party vehicles such as catastrophe bonds and sidecars,” which are, in certain cases, utilised by reinsurers to retrocede some of their business too.
Sidecars have seen strong activity in the last year or two, as reinsurers have found them a useful tool to both leverage for retrocession as well as for growth, by tapping third-party capital sources.
While the primary goal of launching a sidecar now is likely to be as a way to grow, share risks that no longer meet the capital return required by the traditional balance-sheet and to build relationships with third-party investors while benefiting from management fee income, the vehicles provide retro at the same time.
Typically, advises S&P, the less diversified players, or those that focus mostly on writing catastrophe protection purchase a greater volume of retrocession than their more diversified counterparts, owing to the fact that they generally take risk higher in the layers of their reinsurance programmes.
In recent times the retro market has shown signs of experiencing the kind of pricing moderation seen in the catastrophe bond and wider insurance-linked securities (ILS) markets, perhaps supporting the views of those that sense the emergence of a pricing floor.
This could be because a significant proportion of global retrocessional reinsurance capacity comes from the same investors and managers who operate in the catastrophe bond and ILS space, meaning that price declines have moderated in a similar manner.
S&P concludes; “The sector increasingly relies on sound risk management approaches to improve risk-reward analysis when considering whether to remove tail risk from the balance sheet. We expect this trend to continue as an influx of alternative capital continues to weigh on retrocession prices and reinsurers seek to redeploy capital efficiently.”
At a time when the industry is undergoing structural change, driven by ample capacity, intense competition and the broader evolution of the reinsurance market, firms are increasingly looking for ways to diversify, expand and protect their capital.
With market pressures expected to remain and perhaps even intensify, the heightened use of retrocessional reinsurance, via a third-party capital structure or more traditional product, is likely to persist.
Read all of our Monte Carlo Rendez-vous 2015 coverage here.
 View all of our Artemis Live video interviews and subscribe to our podcast.
View all of our Artemis Live video interviews and subscribe to our podcast.
All of our Artemis Live insurance-linked securities (ILS), catastrophe bonds and reinsurance video content and video interviews can be accessed online.
Our Artemis Live podcast can be subscribed to using the typical podcast services providers, including Apple, Google, Spotify and more.































